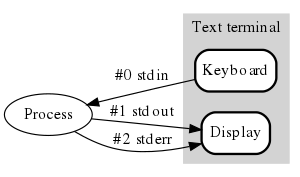
 for input, output, and error
for input, output, and errorIn computing, redirection is a form of interprocess communication, and is a function common to most command-line interpreters, including the various Unix shells that can redirect standard streams to user-specified locations.
In Unix-like operating systems, programs do redirection with the dup2(2) system call, or its less-flexible but higher-level stdio analogues, freopen and popen.
Redirecting standard input and standard output
Redirection is usually implemented by placing certain characters between commands.
Basic
Typically, the syntax of these characters is as follows, using < to redirect input, and > to redirect output.
command1 > file1
executes command1, placing the output in file1, as opposed to displaying it at the terminal, which is the usual destination for standard output. This will clobber any existing data in file1.
Using
command1 < file1
executes command1, with file1 as the source of input, as opposed to the keyboard, which is the usual source for standard input.
command1 < infile > outfile
combines the two capabilities: command1 reads from infile and writes to outfile
Variants
To append output to the end of the file, rather than clobbering it, the >> operator is used:
command1 >> file1
To read from a stream literal (an inline file, passed to the standard input), one can use a here document, using the << operator:
tr a-z A-Z << END_TEXT
one two three
uno dos tres
END_TEXT
To read from a string, one can use a here string, using the <<< operator:
tr a-z A-Z <<< "one two three"
or:
NUMBERS="one two three"
tr a-z A-Z <<< "$NUMBERS"
Piping
Programs can be run together such that one program reads the output from another with no need for an explicit intermediate file:
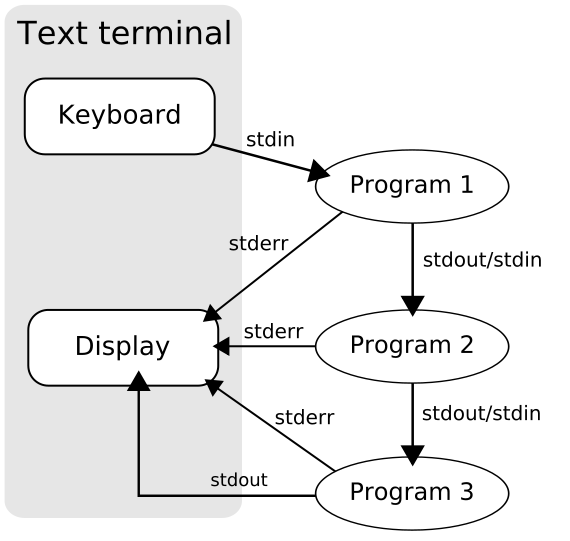
command1 | command2
executes command1, using its output as the input for command2 (commonly called piping, with the "|" character being known as "pipe").
The two programs performing the commands may run in parallel with the only storage space being working buffers (Linux allows up to 64K for each buffer) plus whatever work space each command's processing requires. For example, a "sort" command is unable to produce any output until all input records have been read, as the very last record received just might turn out to be first in sorted order. Dr. Alexia Massalin's experimental operating system, Synthesis, would adjust the priority of each task as they ran according to the fullness of their input and output buffers.
This produces the same end result as using two redirects and a temporary file, as in:
command1 > tempfile
command2 < tempfile
rm tempfile
But here, command2 does not start executing until command1 has finished, and a sufficiently large scratch file is required to hold the intermediate results as well as whatever work space each task required. As an example, although DOS allows the "pipe" syntax, it employs this second approach. Thus, suppose some long-running program "Worker" produces various messages as it works, and that a second program, TimeStamp copies each record from stdin to stdout, prefixed by the system's date and time when the record is received. A sequence such as
Worker | TimeStamp > LogFile.txt
Would produce timestamps only when Worker had finished, merely showing how swiftly its output file could be read and written.
A good example for command piping is combining echo with another command to achieve something interactive in a non-interactive shell, e.g.
echo -e 'user\npass' | ftp localhost
This runs the ftp client with input user, press return, then pass.
In casual use, the initial step of a pipeline is often cat or echo, reading from a file or string. This can often be replaced by input indirection or a here string, and use of cat and piping rather than input redirection is known as useless use of cat. For example, the following commands:
cat infile | cmd
echo $string | cmd
echo -e 'user\npass' | ftp localhost
can be replaced by:
cmd < infile
cmd <<< $string
ftp localhost <<< $'user\npass'
As echo is often a shell-internal command, its use is not as criticized as cat, which is an external command.
Redirecting to and from the standard file handles
In Unix shells derived from the original Bourne shell, the first two actions can be further modified by placing a number (the file descriptor) immediately before the character; this will affect which stream is used for the redirection. The Unix standard I/O streams are:
| Handle | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | stdin | Standard input |
| 1 | stdout | Standard output |
| 2 | stderr | Standard error |
For example:
command1 2> file1
executes command1, directing the standard error stream to file1.
In shells derived from csh (the C shell), the syntax instead appends the & (ampersand) character to the redirect characters, thus achieving a similar result. The reason for this is to distinguish between a file named '1' and stdout, i.e. 'cat file 2>1' vs 'cat file 2>&1'. In the first case, stderr is redirected to a file named '1' and in the second, stderr is redirected to stdout.
Another useful capability is to redirect one standard file handle to another. The most popular variation is to merge standard error into standard output so error messages can be processed together with (or alternately to) the usual output. Example:
find / -name .profile > results 2>&1
will try to find all files named .profile. Executed without redirection, it will output hits to stdout and errors (e.g. for lack of privilege to traverse protected directories) to stderr. If standard output is directed to file results, error messages appear on the console. To see both hits and error messages in file results, merge stderr (handle 2) into stdout (handle 1) using 2>&1 .
If the merged output is to be piped into another program, the file merge sequence 2>&1 must precede the pipe symbol, thus:
find / -name .profile 2>&1 | less
A simplified but non-POSIX conforming form of the command:
command > file 2>&1
is (not available in Bourne Shell prior to version 4, final release, or in the standard shell Debian Almquist shell used in Debian/Ubuntu):
command &>file
or:
command >&file
NOTE: It is possible to use 2>&1 before ">" but the result is commonly misunderstood. The rule is that any redirection sets the handle to the output stream independently. So "2>&1" sets handle 2 to whatever handle 1 points to, which at that point usually is stdout. Then ">" redirects handle 1 to something else, e.g. a file, but it does not change handle 2, which still points to stdout. In the following example. standard output is written to file, but errors are redirected from stderr to stdout, i.e. sent to the screen.
command 2>&1 > file
To write both errors and standard output to file, the order should be reversed. Standard output would first be redirected to the file, then stderr would additionally be redirected to the stdout handle that has already been changed to point at the file:
command > file 2>&1
Chained pipelines
The redirection and piping tokens can be chained together to create complex commands. For example:
sort infile | uniq -c | sort -n > outfile
sorts the lines of infile in lexicographical order, writes unique lines prefixed by the number of occurrences, sorts the resultant output numerically, and places the final output in outfile. This type of construction is used very commonly in shell scripts and batch files.
Redirect to multiple outputs
The standard command tee can redirect output from a command to several destinations.
ls -lrt | tee xyz
This directs the file list output to both standard output and the file xyz.
 persian
persian English (UK)
English (UK)